This course has provided me with some unique opportunities and tool that are relevant for today’s students. With the current changes taking place in education, it is important to meet the needs of our learners in a manner that is relevant to them. With the growing consensus concerning 21st-century skills, students need the opportunity to explore their creativity, critical thinking, communication skills, and collaboration skills. This course has explored some technologies that have provided students with the opportunity to showcase these skills. Some of the tools that were used in this course were blogs, wikis, and podcast. I have always been intrigued about blogs, wikis, and podcasting. I have never had the time to commit myself to learning these new tools. Prior to this course, I had some general knowledge of what a blog, wiki, and podcast were but never created or contributed with these tools.
I have created websites prior to this course both for personal use and professional use. Creating a blog was not much different from creating a website. With the implementation of a blog, I have come to realize the value and potential a blog offers. Blogs, unlike a standard website, provides users the opportunity to engage readers by sharing ideas and posting questions and links. Blogs demand interaction from readers (Richardson 2010, pg. 18). Throughout this course, I had the opportunity to share my thoughts and ideas regarding content and methodology, but more importantly, I have had the opportunity to read other professionals and peers. While we have stressed the importance of student communication and collaboration extensively, professional communication and collaboration are just as valuable. I have committed myself to being a lifelong learner and blogging has provided an avenue to communicate and collaborate with others in my field.
Wikis and podcasting were the two technology tools that were least familiar to me. I did have a general idea of what they were but never created, viewed, or listened to any of them. A wiki space was probably the most intimidating of the three resources. I must admit, when I first learned that “anyone” could create and edit a wiki, I was a little skeptical about the accuracy of the content. In a discussion between Dr. Thornburg and Dr. Hall, they express that the accuracy of Wikipedia rivals that of a conventional encyclopedia. After creating and contributing to our first wiki space, I immediately began brainstorming future uses of a wiki space in my courses. I am currently pursuing the use a wiki space in my Geometry and Robotic courses after the holidays. Podcasting is another great tool I had the opportunity to experience. I was so impressed with experience that I have already introduced podcasting into one of my courses this year. Students are engaged in the process as well as using skills previously mentioned such as communication and collaboration. While they have not presented a final product; what I am hearing sound great. Many students have gone out of their way to present quality work. I am anticipating some wonderful podcast.
Along with developing skills and knowledge about blogs, wikis, and podcast I recognize the value and importance of 21st-Century learning skills. Before beginning this course, my district had already been stressing the values and integration of 21st-Century skills. There has been a concerted effort to move from teacher-centered classrooms to student-centered classrooms. The district has also impressed upon its staff to provide students with opportunities to self-sufficient and active learners. I believe this course as only reinforced these same principles. With resources such as International Society for Technolgy in Education Standards and Partnership for 21st-Century Skills (Laureate Education, n.d.a) I will have the ability to continue my pursuit of implementing technology practices into my classroom. Visiting Partnership for 21st-Century Skills has provided a wealth of information that is pertinent to today’s classrooms. I will continue to visit P21 in the future to further develop my craft.
Dr. Thornburg points out that today’s students are different from learners from the past, and we as a teacher must find ways to meet their needs (Laureate Education n.d.b). The terms digital native and digital immigrants were fairly new to me before this course. Although I was unfamiliar with these terms digital native and digital immigrants, the rationale behind the terms are not. The term digital immigrant was used to identify individuals that were not born into a digital world (Laureate Education, n.d.c). Many of our students would be considered digital natives since most have been influenced by the abundance of technology in their daily lives. Some may consider my generation a digital immigrant due to the lack of technology. I, however, I consider myself more of a digital native due to the comfort of technology and the access that was afforded to me in my younger years. There is often a misconception that digital native and digital immigrant are generational, and this is just not true. Mark Prensky did not intend for the terms digital native and digital immigrant to suggest the level of knowledge one had about technology, but it was rather a metaphor for individual’s attitude and culture. For many years, I have expressed that many students today are not the same type of learners that we were. With the abundance of technology resources at the fingertips of many of our students, they often prefer to utilize this technology into their learning. I have always tried to incorporate technology into lessons, but always maintained focus on the content and not on the technology. The technology should be used to reinforce the students learning and provide opportunities to demonstrate 21st-Century skills.
As I have stated earlier, my district is a strong supporter of learner-centered instruction vs teacher-centered instruction. I am also a strong proponent of student-driven instruction rather than teacher driven instruction. I believe that teacher must encourage students to explore their learning. Exploration will often lead to though provoking questions. Teachers will always provide some level of content knowledge to their students, but we must allow students the opportunity to discover for themselves. It is with this discovery that learning becomes more meaningful to students (Laureate Education, Inc., n.d.a). Dr. Dede mentions that teachers should allow students to gather the information while teachers help students interpret that information (Laureate Education, Inc., n.d.a). We must start teaching students how to learn. Student-driven instruction has many advantages to its implementation, however, it can be a daunting task to implement. The student-driven instruction does take more preparation time for teachers, but the benefits are well worth the effort.
Lifelong learning is crucial in meeting the needs of our students. With the constantly changing landscape of education, it is more important now that teachers stay informed with current technology and resources. In an effort to stay updated and relevant I have chosen to continue my efforts by reading blogs, podcast, and other relevant websites such as P21. I have also chosen to continue my education by pursuing my masters with an emphasis on implementing technology. While there are times that this endeavor can be overwhelming, I understand the importance to myself and my students.
I have set two long-term goals for transforming my classroom environment within the next two years. Goal #1 will be to continue the use and implementation of blogs, wikis, and podcasting. Each of these technologies offers a unique opportunity. I already find myself listening to podcasts and reading blogs more than I ever have. My students have already embarked in creating content using these technologies. I would like to expand their use in the future. Goal #2 is to embrace and implement 21st-centrury skills with the aid of a more learner-centered environment. I have begun to make minor changes in my classroom to address these issues and will continue to do so in the future. Within the next two years, I intend the majority of my class to learner-centered and project based. I am impressed and encouraged after reading about a school district in Manor Texas. Students, after a four-year period, will have participated in over 200 projects. The results of this project based model have proven to be a success. The Manor school district boasts a 98% graduation rate and 100% of these students are accepted into a college (Nobori 2012). With results like these, it is hard not to find value in project-based learning.
After reviewing my checklist from week one, I find that some of my answers have changed. With the aid of this course, I can now progress from sometimes to often in some cases. Two particular areas that show growth is integration and collaboration. I am now more comfortable implementing these technology tools since I have had the opportunity to experience how they are used and created. Collaboration with others has also been beneficial to my growth. Through this collaboration, I have learned that I am not alone in this quest. Many teachers face many of the same challenges and struggles as I do.
References
Richardson, W. (2010). Blogs, wikis, podcasts, and other powerful web tools for classrooms (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin
Laureate Education, Inc. (Producer). (n.d. a). Debate: Digital natives and digital immigrants [Video file]. Retrieved from https://class.waldenu.edu
Laureate Education, Inc. (Producer). (n.d.b). Evolution of technology and pedagogy [Video file]. Retrieved from https://class.waldenu.edu
Laureate Education, Inc. (Producer). (n.d.c). Evolution of technology and pedagogy [Video file]. Retrieved from https://class.waldenu.edu
Nobori, M. (2012, May 23) A Step-by-Step Guide to the Best Projects. Edutopia.com. Retrieved from http://www.edutopia.org/stw-project-based-learning-best-practices-guide




 There are several tools that are available that provides students the opportunity to interact with one another, without having to be in the same location. One possibility, for communication, is the creation of a web page or website. There are currently several sites that provide users the ability to create a free website with little to no technical experience. An alternative to creating a website could be the use of social media. While most would use caution in using personal social media to interact with other peers in an educational setting, there are new educational alternatives. One popular social media alternative specifically for students and teachers is Edmodo. Edmodo provides students and teachers with the same feel of facebook or twitter but in a safer environment. Globester is yet another example of how students can interact with peers in an online format. Blogging and Wiki spaces would also provide students the ability to interact in a unique way. As you can see there are a plethora of tools at the disposal of teachers and students. It is simply a matter of finding what works best for a specific application.
There are several tools that are available that provides students the opportunity to interact with one another, without having to be in the same location. One possibility, for communication, is the creation of a web page or website. There are currently several sites that provide users the ability to create a free website with little to no technical experience. An alternative to creating a website could be the use of social media. While most would use caution in using personal social media to interact with other peers in an educational setting, there are new educational alternatives. One popular social media alternative specifically for students and teachers is Edmodo. Edmodo provides students and teachers with the same feel of facebook or twitter but in a safer environment. Globester is yet another example of how students can interact with peers in an online format. Blogging and Wiki spaces would also provide students the ability to interact in a unique way. As you can see there are a plethora of tools at the disposal of teachers and students. It is simply a matter of finding what works best for a specific application.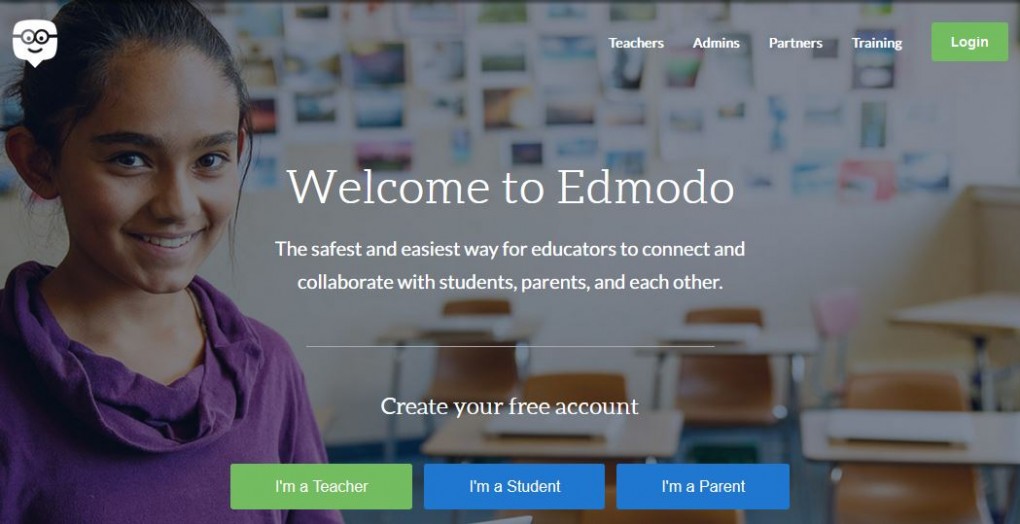 be a short assessment following the lesson. Based on the overall performance of the class they could win a “Free Homework Pass.” Upon completing the assessment via student responses system, results are instantly provided to the class. If students have a collective proficiency level of, let’s say, ninety percent they will each receive a free homework pass. This method encourages students to work collectively to meet a common goal. Another method that has shown promise is the use of badges. The use of a social media like resource called
be a short assessment following the lesson. Based on the overall performance of the class they could win a “Free Homework Pass.” Upon completing the assessment via student responses system, results are instantly provided to the class. If students have a collective proficiency level of, let’s say, ninety percent they will each receive a free homework pass. This method encourages students to work collectively to meet a common goal. Another method that has shown promise is the use of badges. The use of a social media like resource called 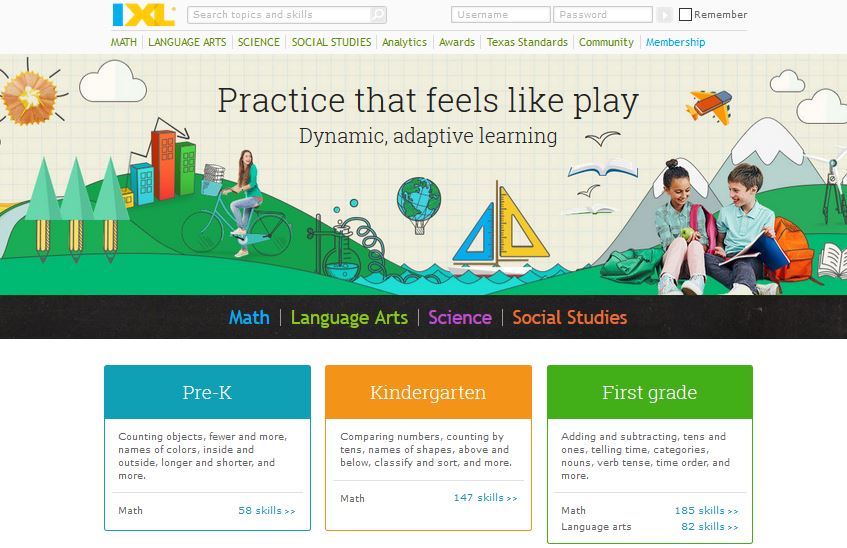 question is dependent on their progress; questions begin easy and gradually become more difficult. If a student misses a question, not only are points deducted but the difficulty level is also reduced. This reduction helps reinforce their prior knowledge before moving on to more challenging problems. To further aid in this reinforcement, detailed instructions are provided to students on the proper procedure to complete this missed problem. The program uses an algorithm to award and deduct points based on difficulty level, meaning questions are weighted differently. In most scenarios, when students miss a question there is no chance of receiving a one-hundred, this is not the case with IXL. Students can still be awarded a one-hundred on the assignment once the lesson as been mastered. As you can see there are many benefits to programmed instruction and how it aids in student performance. While websites such as the one discussed are great resources, it is important to remember that it does not replace other instructional strategies that are provided by teachers. “When students work with computer technology, instead of being controlled by it, they enhance the capability of the computer, and the computer enhances their thinking and learning” (Orey, 2001, sec 4).
question is dependent on their progress; questions begin easy and gradually become more difficult. If a student misses a question, not only are points deducted but the difficulty level is also reduced. This reduction helps reinforce their prior knowledge before moving on to more challenging problems. To further aid in this reinforcement, detailed instructions are provided to students on the proper procedure to complete this missed problem. The program uses an algorithm to award and deduct points based on difficulty level, meaning questions are weighted differently. In most scenarios, when students miss a question there is no chance of receiving a one-hundred, this is not the case with IXL. Students can still be awarded a one-hundred on the assignment once the lesson as been mastered. As you can see there are many benefits to programmed instruction and how it aids in student performance. While websites such as the one discussed are great resources, it is important to remember that it does not replace other instructional strategies that are provided by teachers. “When students work with computer technology, instead of being controlled by it, they enhance the capability of the computer, and the computer enhances their thinking and learning” (Orey, 2001, sec 4). each step of the process without having to watch the entire video. Along with the quick access to each step, students can also find quick links to other videos related to the topic. An example of this might include students working on trig ratio. As students are working on trig ratios there may come a point in which students may need Pythagorean Theorem; Virtual Nerd provides a convenient link to a video on Pythagorean Theorem. This is a great site to use with the flipped model.
each step of the process without having to watch the entire video. Along with the quick access to each step, students can also find quick links to other videos related to the topic. An example of this might include students working on trig ratio. As students are working on trig ratios there may come a point in which students may need Pythagorean Theorem; Virtual Nerd provides a convenient link to a video on Pythagorean Theorem. This is a great site to use with the flipped model.